
continuity and Differentiability some important limits formula YouTube
1. In an open interval (a, b), a function f is said to be continuous if it is continuous at all points in the interval. 2. In an closed interval [a, b], a function f is said to be continuous if f is continuous in (a, b) , lim x → a + f(x) = f(a) , lim x → b − f(x) = f(b) .

Continuity and Differentiability YouTube
x^2 is a parabola centered at the origin..If you take its derivative you get 2x, therefore the derivative of f (x) at 0 would be equal to 0. or you can write as f' (0) = 0..It is a parabola you do not have a hard corner where you would end up with an infinite number of slopes crossing that point.. Comment ( 40 votes) Upvote Downvote Flag

See complete solutions of Miscellaneous Exercise(Continuity & Differentiability) with PDF NCERT
Continuity and Differentiability is an important unit in class 12 mathematics from the perspective of both boards and other competitive exams. It provides in-depth knowledge about the basics of continuity, differentiability, and the relation between them.

Differentiation Formula Continuity and Differentiability Class12 Maths Part 6 Chapter 5
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Formulas Students must thoroughly solve the 5th chapter of NCERT Class 12 Maths, 'Continuity and Differentiability', to excel in Class 12 board exams. NCERT notes Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 is a valuable resource that helps students grasp the step-by-step approach for solving problems, leading to scoring better marks.

SOLUTION Limits continuity differentiability formula sheet mathongo Studypool
Continuity and differentiability are one of the most important topics which make the students understand some of the concepts such as continuity on an interval, continuity at a point, derivative of functions, and etc. 'f' is a real function that has point 'c' in its domain, then 'f' is said to be a continuous function if the value of the functio.
Continuity and Differentiability 1 Math, Calculus, Continuity, Differentiability ShowMe
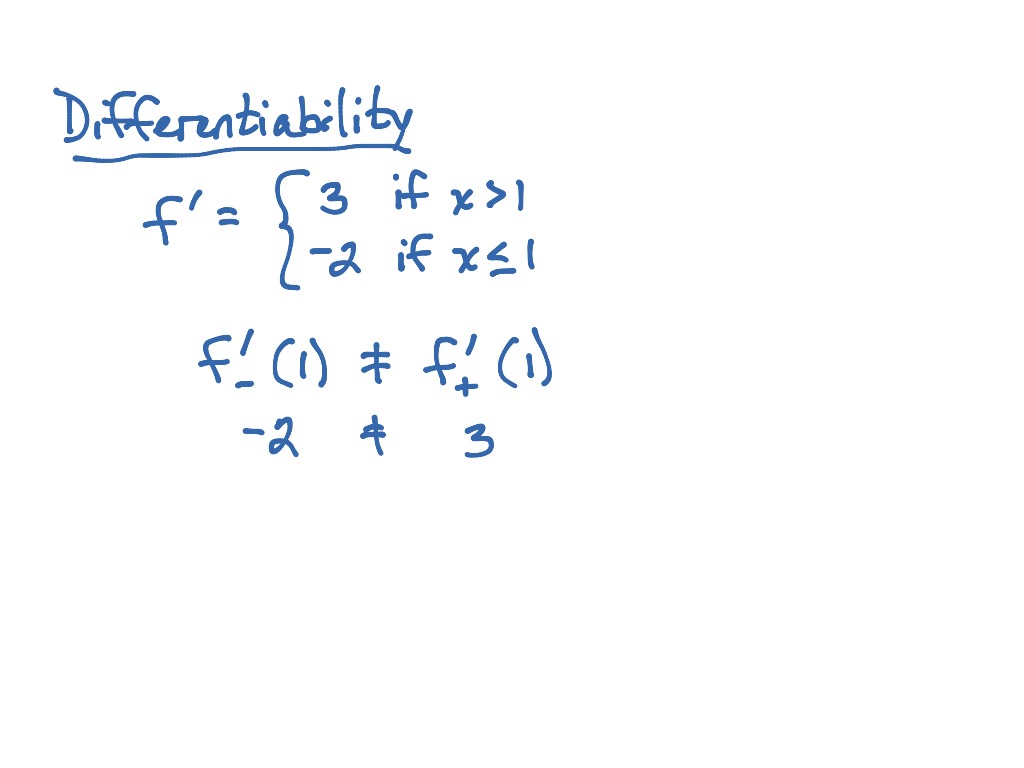
Continuity vs Differentiability. 1. For a function to be continuous lim x → a f ( x) and lim x → a f ( x) = f ( a) for all points a. 2. A function is differentiable anywhere its derivative is defined. A function f ( x) is said to be differentiable at x = c lim x → c f ( x) − f ( c) x − c exists finitely. 3.

Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 formulas Class 12 easy
Mathematically, this is expressed as: f' (c) = lim [x → c] (f (c + h) - f (c)) / h. In simpler terms, a function is differentiable at a point if it has a well-defined tangent line at that point. The tangent line represents the instantaneous rate of change of the function. Also Check - solid shapes Formula Relationship:

Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 formulas Class 12 easy
About Transcript We examine a piecewise function to determine its continuity and differentiability at an edge point. By analyzing left and right hand limits, we establish continuity. Checking the limit of the difference quotient confirms both left and right hand limits are equal, making the function continuous and differentiable at the edge point.

Chapter Continuity and differentiability Class 11 maths formula
It means that a function is differentiable everywhere its derivative is defined. So, as long as you can evaluate the derivative at every point on the curve, the function is differentiable. How To Determine Differentiability By using limits and continuity! The definition of differentiability is expressed as follows:

Chapter Continuity and differentiability Class 11 maths formula
The continuity of a function and the differentiability of a function are complementary to each other. The function y = f (x) needs to be first proved for its continuity at a point x = a, before it is proved for its differentiability at the point x = a.

Chapter Continuity and differentiability Class 11 maths formula
"Continuity and Differentiability One Shot Video: https://youtu.be/3v--OCXUgYYTimestamp:00:00 Introduction00:53 Continuity03:17 Algebra of Continuity 04:01 C.

Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 formulas Class 12 easy
Get NCERT Solutions of Class 12 Continuity and Differentiability, Chapter 5 of NCERT Book with solutions of all NCERT Questions.. The topics of this chapter include. Continuity. Checking continuity at a particular point,; and over the whole domain; Checking a function is continuous using Left Hand Limit and Right Hand Limit; Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division of Continuous functions

V D U Full Form In Hindi Stairs Design Blog
Theorem 1: Algebra of continuous functions: If the two real functions, say f and g, are continuous at a real number c, then (i) f + g is continuous at x=c.

Differentiability Introduction Formula/Basic/Graph Continuity and Differentiability Lecture
CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY vThe whole of science is nothing more than a refinement of everyday thinking." — ALBERT EINSTEIN v 5.1 Introduction This chapter is essentially a continuation of our study of differentiation of functions in Class XI.
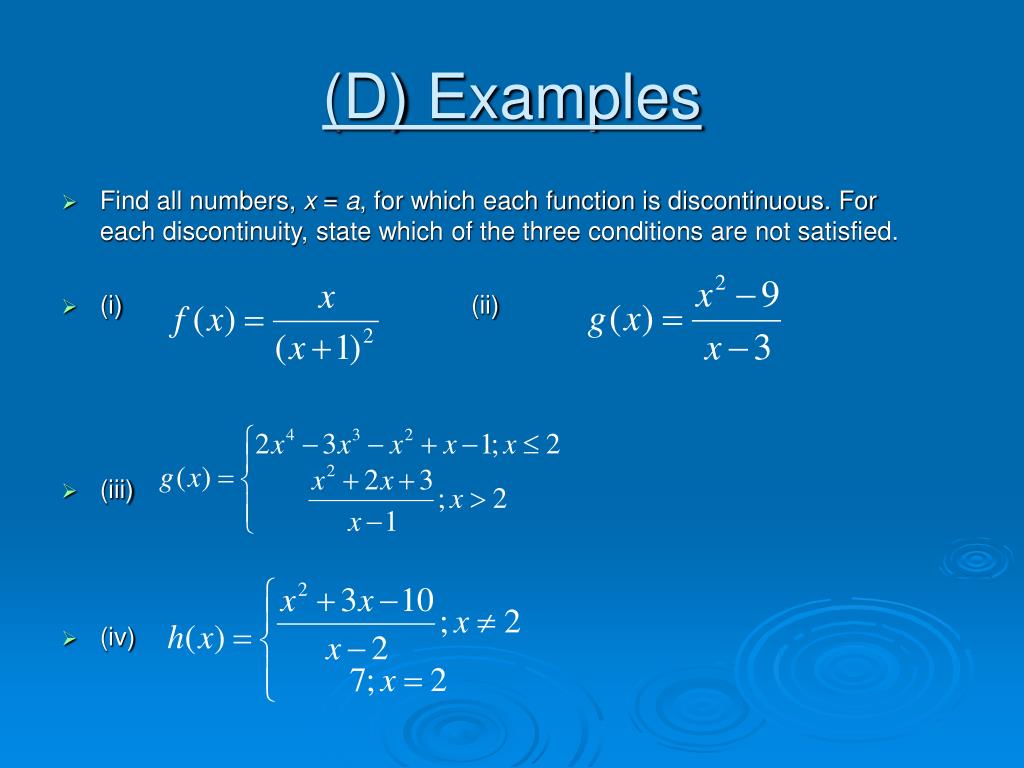
PPT BCC.01.9 Continuity and Differentiability of Functions PowerPoint Presentation ID257105
Quiz Unit test Continuity and differentiability Intuition for the definition of continuity Continuity of a function using only definition

Formula Sheet Of Chapter 5 Continuity & Differentiability Class 12 Maths Notes LearnPick India
To understand the principles of continuity and differentiability, students should become familiar with the relevant mathematical formulas. Theorems on Continuity and Differentiability. Theorem 1: If two functions f(x) and g(x) are continuous at a real valued function and continuous at a point x = c, we have: